A foundation that fits just right gives superconducting nickelates a boost
It irons out wrinkles in thin films of these novel superconductors so scientists can see their true nature for the first time.
By Glennda Chui
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University say they’ve found a way to make thin films of an exciting new nickel oxide superconductor that are free of extended defects.
Not only does this improve the material’s ability to conduct electricity with no loss, they said, but it also allows them to discover its true nature and properties, both in and out of the superconducting state, for the first time.
Their first look at a superconducting nickel oxide, or nickelate, that does not have defects revealed that it is more like the cuprates – which hold the world’s high-temperature record for unconventional superconductivity at normal pressures – than previously thought. For instance, when the nickelate is tweaked to optimize its superconductivity and then heated above its superconducting temperature, its resistance to the flow of electric current increases in a linear fashion, just as in cuprates.
Those striking similarities, they said, may mean these two very different materials achieve superconductivity in much the same way.
It's the latest step in a 35-year quest to develop superconductors that can operate at close to room temperature, which would revolutionize electronics, transportation, power transmission and other technologies by allowing them to operate without energy-wasting electrical resistance.
The research team, led by Harold Hwang, director of the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) at SLAC, described their work today in the journal Nature.
“Nickelate films are really unstable, and until now our efforts to stabilize them on top of other materials have produced defects that are like speed bumps for electrons,” said Kyuho Lee, a SIMES postdoctoral researcher who contributed to the discovery of superconductivity in nickelates four years ago and has been working on them ever since.
“These quality issues have led to many debates and open questions about nickelate properties, with research groups reporting widely varying results,” Lee said. “So eliminating the defects is a significant breakthrough. It means we can finally address the underlying physics behind these materials and behind unconventional superconductivity in general.”
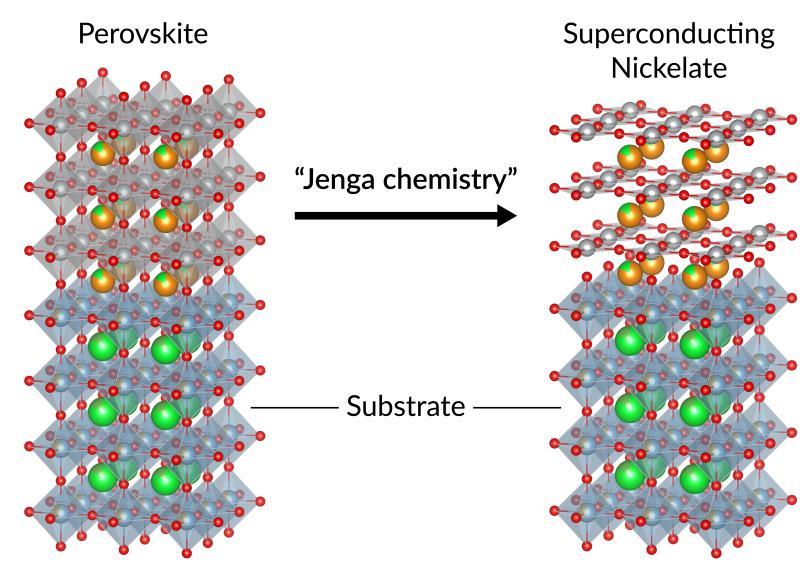
Jenga chemistry and a just-right fit
The defects, which are a bit like misaligned zipper teeth, arise from the same innovative process that allowed Hwang’s team to create and stabilize a nickelate film in the first place.
They started by making a common material known as perovskite. They “doped” it to change its electrical conductivity, then exposed it to a chemical that deftly removed layers of oxygen atoms from its molecular structure, much like removing a stick from a tower of Jenga blocks. With the oxygen layers gone, the film settled into a new structure – known as an infinite-layer nickelate –that can host superconductivity.
The atomic latticework of this new structure occupied a slightly bigger surface area than the original. With this in mind, they had built the film on a foundation, or substrate, that would be a good fit for the finished, spread-out product, Lee said.
But it didn’t match the atomic lattice of the starting material, which developed defects as it tried to fit comfortably onto the substrate – and those imperfections carried through to the finished nickelate.
Hwang said it’s as if two friends of different sizes had to share a coat. If the coat fit the smaller friend perfectly, the larger one would have a hard time zipping it up. If it fit the larger friend perfectly, it would hang like a tent on the smaller one and let the cold in. An in-between size might not be the best fit for either of them, but it’s close enough to keep them both warm and happy.
That’s the solution Lee and his colleagues pursued.
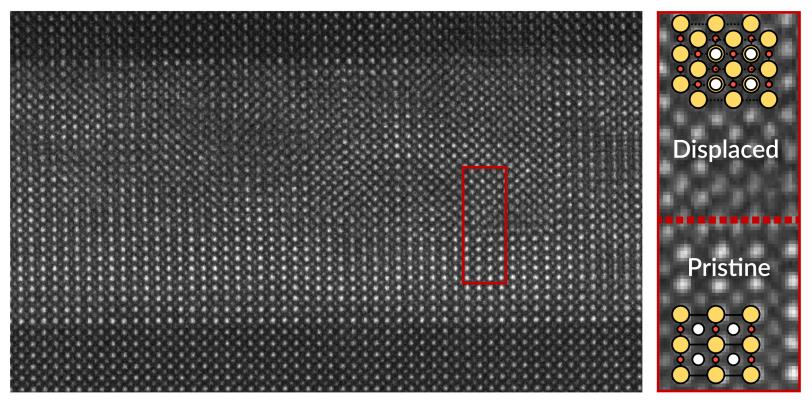
In a series of meticulous experiments, they used a substrate that was like the in-between coat. The atomic structure of its surface was a close enough fit for both the starting and ending materials that the finished nickelate came out defect-free. Lee said the team is already starting to see some interesting physics in the nickelate now that the system is much cleaner.
“What this means,” Hwang said, “is that we are getting closer and closer to measuring the intrinsic properties of these materials. And by sharing the details of how to make defect-free nickelates, we hope to benefit the field as a whole.”
Researchers from Cornell University contributed to this work, which was funded by the DOE Office of Science and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Systems Initiative.
Citation: Kyuho Lee et al., Nature, 12 July 2023 (10.1038/s41586-023-06129-x)
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
About SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by researchers around the globe. As world leaders in ultrafast science and bold explorers of the physics of the universe, we forge new ground in understanding our origins and building a healthier and more sustainable future. Our discovery and innovation help develop new materials and chemical processes and open unprecedented views of the cosmos and life’s most delicate machinery. Building on more than 60 years of visionary research, we help shape the future by advancing areas such as quantum technology, scientific computing and the development of next-generation accelerators.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.